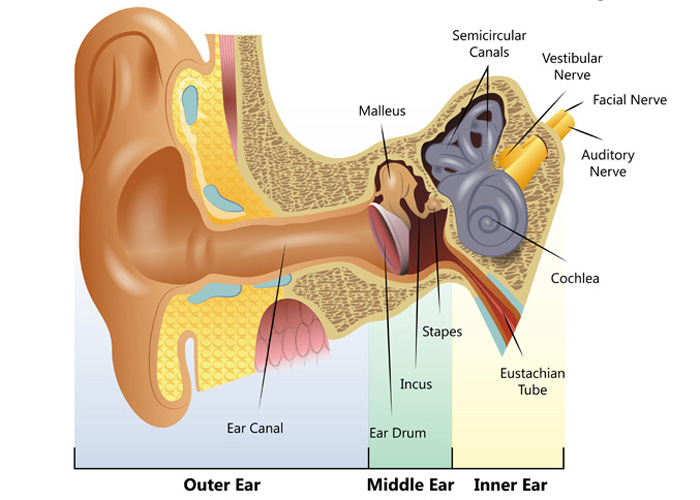
*AUDITION-(EAR)
human ear consist of external ear:-pinna,auditory meatus,
middle ear:-ear osscicles
muscles:-tensor tympani
stapedius
eustachian tube
inner ear :-cochlea,circular canal
-function middle ear-
transmission of sound wavees from outer ear to internal ear
-impedence matching:-
-sound waves when travel from air media to liquid there is loss of intensity-this is compensated by following method 1)vibration of malleus ,incus,stapes amplify the sound waves by 1.3 times
2)surface area of tympanic membrane is 50mm^2 and that oval membrane 3mm^2 so,the the pressure at the wondow is 17 times greater
so, net pressure at oval window and loss of intesity is compensated this matches with the loss of energy from one media to another
3)tympanic reflex-protective reflex prevents damage to inner ear
- tensor tympani attached to the neck of malleui contracts and moves inward
lous sounds entering inner ear is prevented
eustachin tube:-connects middle ear to naso pharynx
tries to equalise the pressure on the either side of tympanic membrane
-masking effect:-even though there is noise in envirnment ,the individual can hear his on voice due to this effect
*deafness:-inability to hear
types :-conductiondeafness,and neural deafness
1)conduction deafness:wax hardened
foreign substance
perforation in the tympanic membrane
-tumor
2)neural deafnes: lesion in auditory nerve
-lesion in auditory cortex
-explosives, occupational hazards
-drugs use of antibodies like streptomyosin,gentamyosin
test:-
whisper test
stop watch test
tuning fork test -rinner's test,weber's test}for partial suffering from condition or neural deafness
-audiometry-extent of hearing loss
rinners test:-normal person}air condition is better AND LONGER THAN BONE CONDUCTION
the conduction deafness :air conduction is absent
in normal deafness :air conduction is present after bone conduction
webers test:-in normal person :-sound is hear equally on both ears
the conduction deafness affected ear heard louder
in neural deafness affected ear cannot hear
human ear consist of external ear:-pinna,auditory meatus,
middle ear:-ear osscicles
muscles:-tensor tympani
stapedius
eustachian tube
inner ear :-cochlea,circular canal
-function middle ear-
transmission of sound wavees from outer ear to internal ear
-impedence matching:-
-sound waves when travel from air media to liquid there is loss of intensity-this is compensated by following method 1)vibration of malleus ,incus,stapes amplify the sound waves by 1.3 times
2)surface area of tympanic membrane is 50mm^2 and that oval membrane 3mm^2 so,the the pressure at the wondow is 17 times greater
so, net pressure at oval window and loss of intesity is compensated this matches with the loss of energy from one media to another
3)tympanic reflex-protective reflex prevents damage to inner ear
- tensor tympani attached to the neck of malleui contracts and moves inward
lous sounds entering inner ear is prevented
eustachin tube:-connects middle ear to naso pharynx
tries to equalise the pressure on the either side of tympanic membrane
-masking effect:-even though there is noise in envirnment ,the individual can hear his on voice due to this effect
cochlea:-
-it is a coiled structure
-recepters of hearing-hair cells - present in organ of corti of basillar membrane
-
-hair cells which are the receptors of hearing in the organ of corti
-the chamber are scala vestubili has perylymph,scala media has endolymph and tunnel of corti formed by inner and outer corti
outerside of outer rod of corti has 3 rowes of hair cells ,supprting cells are present in between hair cells
-whenever hair cells get destroy supprting cells form new
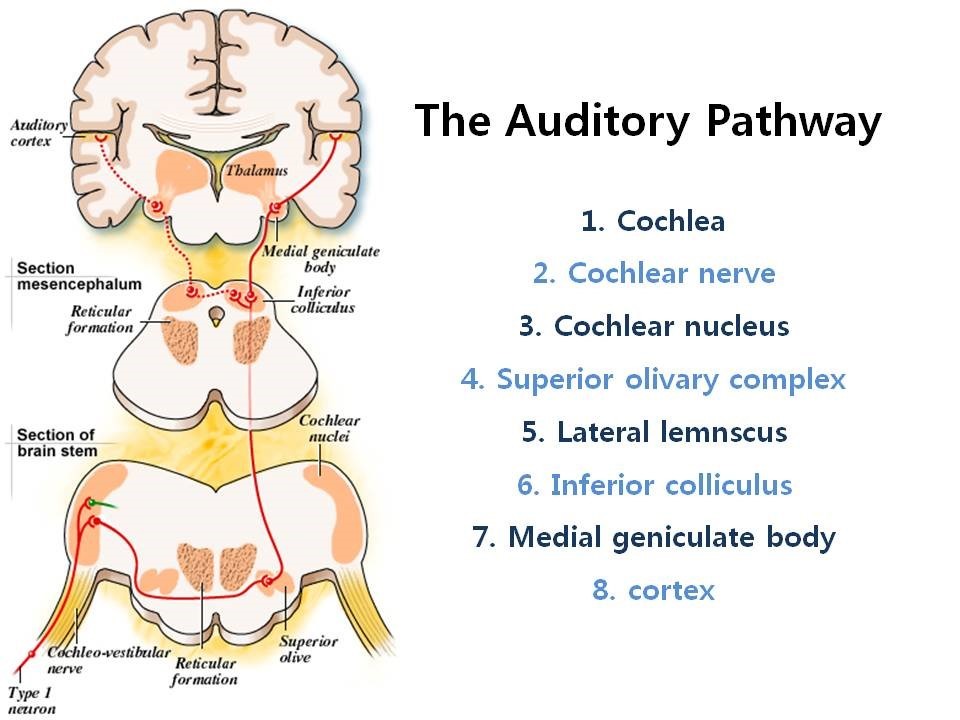
* auditory pathway:-
*deafness:-inability to hear
types :-conductiondeafness,and neural deafness
1)conduction deafness:wax hardened
foreign substance
perforation in the tympanic membrane
-tumor
2)neural deafnes: lesion in auditory nerve
-lesion in auditory cortex
-explosives, occupational hazards
-drugs use of antibodies like streptomyosin,gentamyosin
test:-
whisper test
stop watch test
tuning fork test -rinner's test,weber's test}for partial suffering from condition or neural deafness
-audiometry-extent of hearing loss
rinners test:-normal person}air condition is better AND LONGER THAN BONE CONDUCTION
the conduction deafness :air conduction is absent
in normal deafness :air conduction is present after bone conduction
webers test:-in normal person :-sound is hear equally on both ears
the conduction deafness affected ear heard louder
in neural deafness affected ear cannot hear

Comments