human excretion :-it is the process of excreting waste such as creatinine,uric acid,ammonia
kidneys-primary excretory organ-urine
skin-supplementary organ-sweat
salivarygland-supplementary organ-saliva
lungs-supplementary organ-co2,h20
*function of kidney:
1)excreation of metabolic waste -NH3,urea,uricacid,creatinine
normal count of urea:-15-40mg%
of uric acid-3-7mg%
of creatinine-0.7-1.4mg%
2)regulation of blood volume &blood pressure
3)synthesis of vit d3
4)maintaining electrolyte balance
5)JG cells :produce renin for regulatoryblood pressure
*Nephron:-
structural and functional unit of kidney

kidneys-primary excretory organ-urine
skin-supplementary organ-sweat
salivarygland-supplementary organ-saliva
lungs-supplementary organ-co2,h20
*function of kidney:
1)excreation of metabolic waste -NH3,urea,uricacid,creatinine
normal count of urea:-15-40mg%
of uric acid-3-7mg%
of creatinine-0.7-1.4mg%
2)regulation of blood volume &blood pressure
3)synthesis of vit d3
4)maintaining electrolyte balance
5)JG cells :produce renin for regulatoryblood pressure
*Nephron:-
structural and functional unit of kidney

there are two types loops:cortical (short loop of henley )
:juxta medullary (long loop)
cortical:1)more in number-80%
2)short loop of henley
3)efferent arteriol
4)formation of urine
juxta medullary:-1)less in number
2)large loop
3)vasa recta u shaped
4)concentration of urine
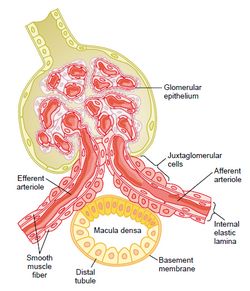
*juxta medullary apparatus:-
when the DCT of juxta medullary nephrones come in contact with its own glomerolus the modified structure is known as JGA
1)JG CELLS- modified cells of afferent arteriol
-produce renin which can regulate BP
-for regulation of erythropoeosis in case of hypoxia
2)MACULA DENSA- modified cells of DCT
-asses the concentration NA in urine
3)LACI'S CELLS:-(mesengeal cells) -modified cells at the shear junction formed by afferent arteriol and efferent artriol &DCT
*Renal blood flow:-
1)ultra filtration
2)reabsorbtion
3)tubular secretion
1)ultra filtration;-by the filtrane membrane (formed by fusion of capillary wall of bowmans capsule)
2)GFR :-definition:- total amount of ultrafiltrate formed by all the nephrons of both the kidney per unit time is called glomular filtrate
normal value:-125ml/min
factors affecting renal blood flow:-
1)glomerular capillary pressure
2)collidal osmotic pressure
3)tubular hydrostatic pressure
4)total surface area of filtrating membrane
5)renal blood flow amount
6)total number of nephrones
*Plasma fraction:- It's the ratio between GFR &plasma flow
=GFR/RPF
=125 MIL/MIN/660ML/MIN
1/5MIL/MIN
selective reabsorption:-
1)high threshold substance-glucose,amino acid
2)low threshold substance-water1%,urea5%
3)non threshold substance-creatinine
water reabsorbtion in renal tubule-
-GFR-180L/DAY-1.5L/DAY LOST AS URINE
-178.5 L/DAY-reabsorbed of water -renal tubule
*method of reabsorption of water -renal tubule
obligatory reabsorbtion:-
for the sake of NA,H20 is being reabsorbed
-becuase of aldesterone action
-80%
-PCT &HENLES LOOP reabsorbtion occurs
*faculatory reabsortion:-
ADH action water absorbtion
-20%
DCT & collecting duct
*handling of glucose in renal tubule
-glucose small molecules so, it passesthrough the filtering membrane .everything in the ultrafiltration cant be afford to loose in urine
-if lost the condition is called glycosuria
-it should totally reabsorbed
*renal threshold for glucose :-
glucose in blood abouve which appears in the urine
the normal value=160-180MGM%
above 180 -diabeties in urine
*Transport maximum for glucose
it is the max. rate at which transport of glucose molecule occurs inthe renal tubule
-Normal value:380mgm/min
above ,it is seen in urine
*Reabsorbtion of NA in renal tubule:-
99%$ is reabsorbed 1% is lost in urine
-method by which NA is reabsorbed
:co-transport along with glucose
:NA+ K+ pump
:aldesterone
:passive transport
*transport of urea:-
-50% lost -50% reabsorbed
-method-countercurrent mechanism
-occurs in u shaped -henles loop &vasarecta
:normal urea-15-40
*Tubular secretion:--substance that cannot be retained should be lost in urine
-it get secreted inner lining cells of tubule
eg:creatinine,PAH
*constitents of urine analysis;-
-abnormal constituents :-
-albuminuria -loss of albumin in urine
eg:pregnancy ,kidneydisfunction
-glycosuria-eeg:diabeties melitus
-ketonuria-breakdown of fats /fatty acid
-haematorea-traces of blood in urine -eg:internal bleeding
-bilirubinurea-loss of bilirubin-due to juandice
*Skin:-
function-
act as supplementory excreatory organ
:electrolytes,urea ,some amount of H2O -sweat
-:Regulation of body temprature-
-body heat is conserves:-(winter)
:vasoconstiction
:shivering
:basal metabolic rate is increased
:adipose tissue helps in conserve heat
-body heat is lost(summer):-
:vasodialation-sweating
:BMR is decrease T4 also decreased
-cutaneous receptors in skin:-
:touch, pressure ,pain,temprature
-protective covering-melanin
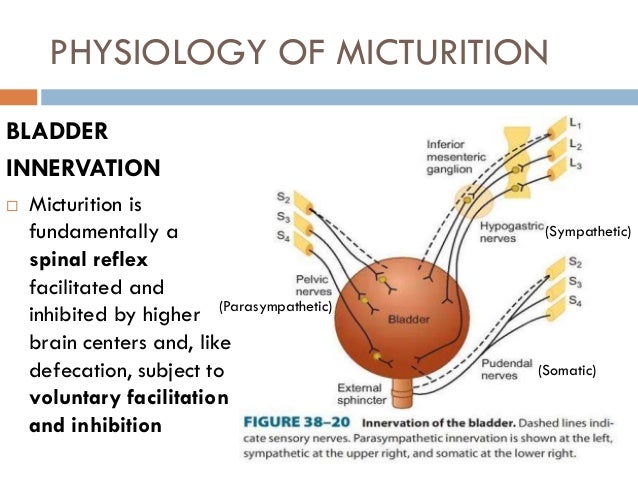
*micturation reflex:-
:voiding or elimination od urine collected in bladder through urethra is called micturition
:it is a reflex process which have S2,S3,S4,spinalcord
:higher center includes medulla oblangatta ,pons,&cerebral cortex which is always inhibitory
:-Urinary bladder:-it has structure called trigone made up of special muscle called detrouser
tigone continue as internal spincter which is involuntary .the urethra also guarded by voluntary by external spincter
-urinary bladder and internal urethral bladder is innervated by both parasympathetic &sympothetic innervation
-parasympathetic innervation-helps in emptying by bringing about contaction of UB &relaxation of internal spincter
-sympathetic innervation-helps in filling UBby relaxation of UB &contraction of internal spincter
-in newborn becuase of non- mylinated of nerve fibers filling&emptying automatic
-atomatic bladder:-
cuase-injury above the sacral segment
symptom;-filling and emptying without control
-atonic bladder:-
injury at sacral segment
:tonicity of detroser muscle is lost leads to incontinence &drifting of urine
-cystometrogram:-
its a graph showing relationship between volume of urine collected UB
phase I:-
it is a linear graph up to 100 ml of urine collected there is gradual increase in pressure
phase II:-
it is a plateu phase ,urine is collected in nUB PRESSURE REMAINS SAME (UP TO 400 ML)
phaseIII
as the vol. increases in UB pressure also increases
: the detrouser muscle loss its adaptation to relax &urine is collected up to 600 ml
micturition becomes in avodable and painful
-counter current mechanism:-
-significance :-to ensure concentration of urine
-to mainatin gradient in medulla
-to maintain the hypermolarity inner medulla
mechanism:-whatever happens in ascending limb its opposite should happen in descending limb
renal function test:-
-its a test to asses the function of kidneys
-there are four type of test
:blood analysis:-glucose(80-140mg%
:urea-15-40mg%
:creatinine 0.7-1.4mg%
-radiological analysis:xray
ultrasound scaning
_clearance test :it is the amount of plasma required to clear off the substance which introduced for unittime
:-criteria for the substance-inert:shouldnt dilute with blood
non toxic substance should be selected
freely filterd in glomerules
shouldnt be reabsorbed in renal tubule
shouldnt be secreted in renal tubule
:-inulin:-Cin(inulin)=uv/p,
where u=volume of urine =2ml/min
v=inulin pressure in urine =1.25mg/ml
p=inulin pressure in plasma
Cin =1.25*2/0.02=2.5/0.02=125ml/min}GFR
Significance of inulin:-
its useful in calculating GFR
-I IS EQUAL TO gfr BECUASE NEITHER REABSORBED IN RENAL TUBULE NOR SECRETED
:-clearance test using urea:-Curea=60ml/min(50% reabsorbed )
credits:-physiotherapycls.com



Comments